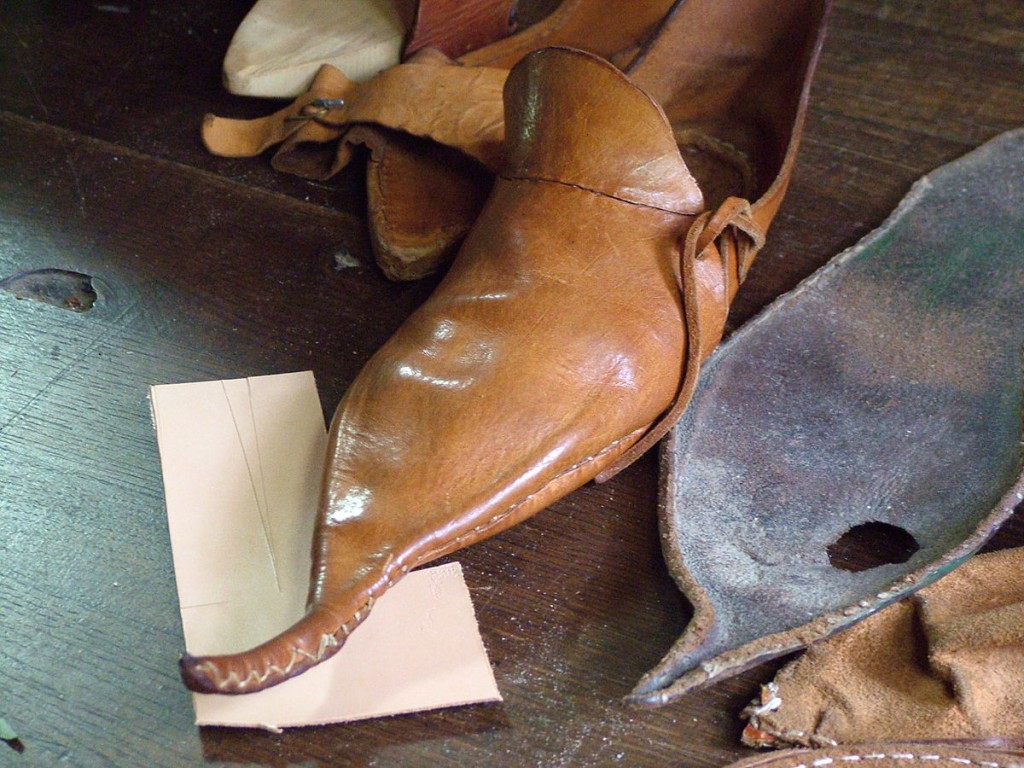
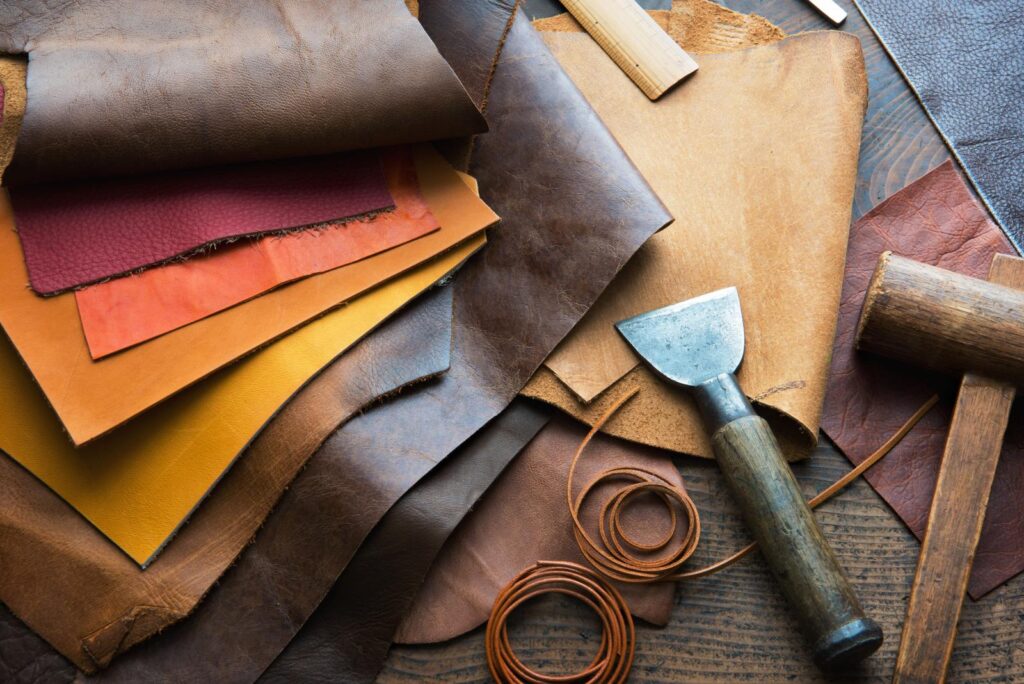
Leather is the most useful and earliest discovery, used by people in every corner of the world. The history of leather involves different times when people discovered various uses for leather. These include clothing, shoes, handbags, tools, equipment, and crafts.
How the history of leather started?
Initially, the historical journey of leather can be traced back to around 400,000 years ago in England.
The historical evolution of leather began through different ages including the Stone, Bronze, and Iron ages, then Ancient Times, Middle Ages, and after that the Renaissance, the Industrial Revolution, and into modern times.
Let’s explore the historical journey of leather through these ages till modern times.
Evolution of leather crafting:
In early times, man has been using leather for survival. The hides and skins of animals are used to make different tools for a better living such as leather shoes used for walking.
Man has used leather fur to keep warm in colder climates while these animal hides are used for shelter in warmer conditions.
Leather crafting is based on a specific function of leather.
As time passed societies built up and man evolved so are the uses of leather. It involves leather armor, jewelry, harnesses, boots, tents, satchels, and writing surfaces. In some cultures, leather became a status symbol because of its visual appeal and function.
Over time, leather has become a must-have in everyone’s life. The mass production of leather shoes, gloves, jackets, and accessories has become available to people. Leather crafting has become an industry.
It is incredible to see how leather crafting has evolved and how leather goods have been used widely everywhere.
Leather History in the Stone Age (Pre-History to 3000 BC):
The stone age is one of the most prolonged periods in the history of leather. It covered millions of years though we see evidence of leather crafting and working around 400,000 years ago.
The early stone tools known to date were 3.3 million years old. They were flakes of stone that might use for cutting and scraping the hides of animals.
The stone scraping tools were found in Hoxne, England. Researchers have examined the microscopic wear patterns on these scraping tools and concluded that they would have been used to scrape animal hides. This scraping would help them to prepare hides for preservation, tanning, and usage.
From a few hundred thousand years ago to 82,000 BC, bone awls have been seen in South Africa. These bone awls might have been used to make holes in leather hides. Clothing and shelters would have been made by combining these leather hides and furs.
In Siberia, around 33,000 BC, the first sewing needles having an eye to pass thread or some other related material, were found. This showed a dramatic shift in leather crafting from using awls to making holes and needles to pass through them along with the thread. More items of daily use could have been made and repaired. Fats could be rubbed on leather hides to make them waterproof.
- The oldest leather tanning operations were found around 5000 BC in Sumer (modern-day Iraq).
- The oldest leather shoe with laces was found around 3,500 BC in Armenia.
- Leather has been used to make couplings and chariot harnesses since around 3,100 BC in ancient Egypt.
More leather was used with the faster growth of civilization, leading to the Bronze Age.
Leather History in the Bronze Age (3000 BC – 1200 BC):
Stone tools remained popular in the Bronze Age.
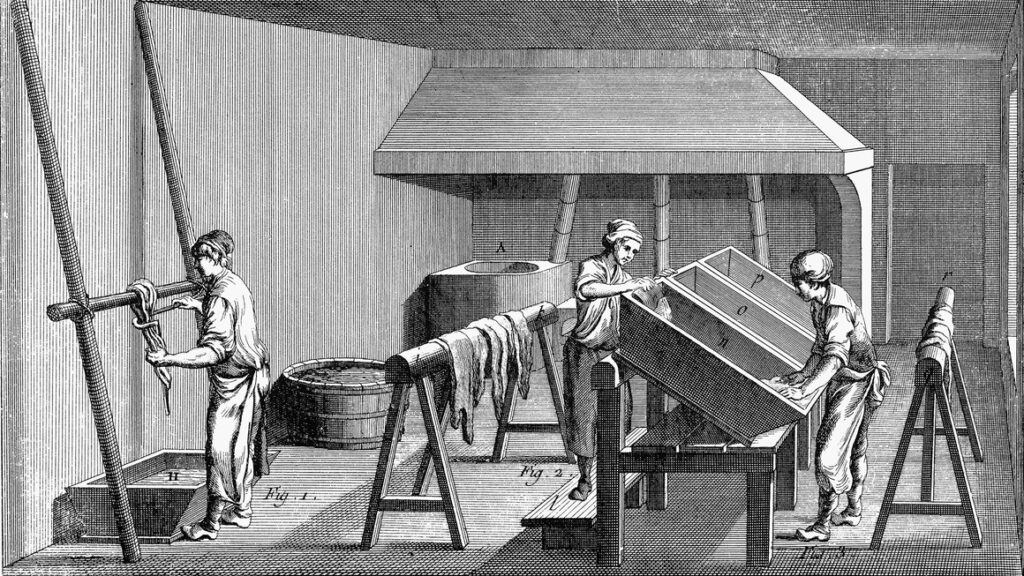
Trade started with advancements in technology. With increased trade, the evolution of tanning animal hides into leather started. As tanning becomes advanced, so does the crafting of leather. Leather has started to be used in making various goods, for example, from shoes to hats, capes, belts, shelters, and shields to arm protectors.
Following are some large advancements in the leather craft in this period:
- The Discovery of the leather shoe was around 1300 BC. This shoe has made from one piece of leather, having holes for laces. The back of the shoe is also laced up.
- Use of different tools to remove hair from leather to give it a smooth finish.
- Fine combs were made from bone to give a finish to the leather’s surface.
Leather History in the Iron Age (1200 BC – 550 BC):
During Iron Age, the population increased as communities continue growing. Farming became more advanced for accessing food and other resources. With an increase in population, there was increased demand for leather goods.
Small cities became larger. Colorful clothing became popular among people along with leather shoes and sandals having laces.
Leather can be degraded and disintegrated over time when exposed to elements and there’s an example of a leather armband that was found around the end of the Iron Age.
This band was worn by “Old Croghan Man”, (height 6’ 6’)’. His fingernails were well-groomed. He wore a braided armband on his upper arm. The band includes bronze mounts that held the leather together and also served a decorative purpose. This discovery showed that leather was worn by people thousands of years ago. It is evident from this, that leather craft was evolving.
Leather History in Ancient India (3000 BC – 600 BC):
The Indian culture is integrated very closely into world history. In ancient India, leather was very much valued. The early Hindu scriptures were written in Sanskrit and captured in a volume called “Vedas”.
Around 3000 BC, mentioned in Rig-Veda, there is a reference to the use of leather items such as bottles and mashaks (water-carrying bags). Other literary references mentioned the use of items made from leather such as leather laces, straps, and bands. With this evidence, it was clear that leather was very much needed during this period.
Leather History in Ancient Egypt (2700 BC – 350 BC):
In this era, we see more specialized and widespread use of leather.
Generally, Ancient Egyptians wore pieces of very light clothing due to the warm climate conditions. So, at this time, leather accessories were available such as leather sandals but these were worn by wealthy individuals.
Here are some other uses of leather in this period:
- Chariot harnesses and couplings were made from leather and fashioned from a strong material.
- Leather jewelry was available to the wealthy.
- Interestingly, the leather was used as a writing surface. There were examples of Egyptian manuscripts made of leather. They are long leather rolls on which words and images are inscribed.
Researchers also found that plant-based processes of leather tanning originated in Egypt.
Leather History in Ancient China (1600 BC – 200 BC):
Chinese civilization has been very advanced since ancient times. The history of China goes back thousands of years ago and so does the history of leather.
Like other cultures at that time, China used to make shoes from leather and lately, leather boots.
Chinese leather armor holds much importance in the history of leather in China. Leather armor was used for protection during battles. These leather armors were custom-fit and made from cow, buffalo, and rhinoceros hides.
Here are some significant ways in which leather armor was used:
- Leather crafters made leather tunics for warriors.
- Leather armor was used to make helmets and shields.
- Full-armor suit for horses was also crafted to protect both soldier and horse during the battle.
Leather History in Ancient Greece (800 BC – 200 BC):
The people in Greece enjoyed the warm climate and so most clothing consists of light linen tunics. They were not always worn shoes but when needed and for protection, they preferred laced-up leather sandals.
It is believed that the Greeks developed the vegetable tanning process. It may begin in Egypt and the knowledge further spread. Rome would have adopted it later. The vegetable tanning process involves processing the leather using natural tannins.
Greeks used leather for various items such as sandals, bags, shields, and protective wear. Leather straps and supports were used by chariots and cavalry/military units.
Leather History in Ancient Rome (750 BC – 500 CE):
Rome is one of the most advanced and complex civilizations in history.
By this time, there were social structures built up that allow the specialized and high-volume production of different items need for clothing, food, and personal accessories.
Mostly, animal hides came from butchers. Romans utilized a new method of tanning, called “Alum Tanning”, along with the vegetable tanning method. Alum is a salt compound that helps to produce soft leather.
Leather was a common and useful material in the Roman Empire. Here are some common uses of leather in ancient Rome:
- It was used in high volumes for the Roman army.
- Leather reins and straps would be needed by horses.
- Leather fixtures would be needed by chariots.
- Soldiers would need leather boots, sandals, belts, and for protective equipment.
Leather History in the Dark Ages (500 CE – 800 CE):
Leather crafting became more advanced in the Dark Ages. The uses of leather increased and so does the skills used to craft with it became more refined.
The two main advancements in leather craft include
- Shoes were made from different pieces of leather and were more closed in design.
- The leather started being used for the backs of chairs and seats. A soft material is used behind the leather for durability and comfort.
Leather History in the Viking Age (800 CE – 1000 CE):
Vikings used leather for different purposes extensively. Leather was frequently used for accessories and footwear. Styles of shoes varied greatly and offered different looks, fits, and levels of protection.
The common uses of leather in the Viking Age were:
- Ankle and calf boots became popular.
- Laces made of leather were wrapped around the footwear to keep them in a secure position.
- Leather hats were made for retaining heat during cold weather.
- Bags and belts were common items made of leather. Pouches were made to carry small personal items.
- Leather was also used for protective and military uses. Vikings made different items that include sword scabbards, shields, knife sheathes, helmets, straps, slings, saddlery, and some protective garments.
Leather History in the Middle Ages (1000 CE – 1300 CE):
Middle Ages saw continued growth in the popularity and crafting of leather.
Major advancements include
- At this time, more leather processing practices evolved such as tooling, dyeing, carving, and painting.
- A method called applique was used in which items were attached to leather for decorative and functional purposes.
- Boar bristles were used as needles. They are strong, flexible, and thick so easily pass through leather materials while pulling the thread.
- Advancements were seen in sewing techniques and threads.
- Specialized tools for leather became popular.
- The Crakow Shoe was designed in the Middles Ages and became a very popular trend. The shoe has an elongated curved end with a pointed tip. Its function was considered important socially. The more curved the toe has, the higher the social class of a person was.
- Leather trade associations started to form.
Leather History in the Renaissance (1300 CE – 1650 CE):
During the Italian Renaissance, the world saw vast intellectual progress. Leather crafting, use, and tooling expanded.
Here are some major advancements at this time:
- Leather was utilized in the ornamental seating. This turned the basic chairs into status symbols and pleasing sights.
- Leather associations became more popular.
- Tanning industries were built in Tuscany and Florence.
- The molding, shaping, and stamping of leather was performed for function and art.
- Due to increased global trade, leather processing, and crafting became more specialized and refined.
- Leather was used for various items such as shoes, bags, belts, clothing, hats, pants, overcoats, capes, cloaks, book bindings, and satchels.
- For military needs, leather straps and ties were used.
- Finished goods of leather and leather accessories were considered materials of the upper class.
Leather History in the Enlightenment (1650 CE – 1760 CE):
The Enlightenment saw a bit shift in leather and leather crafting from the technical evolution of items to the socio-political side. At that time, while leather industries were established across the world, and major world powers have been controlling and settling new lands, the main focus was on controlling the production and distribution of leather and its commercial side.
In 1700, England tried to put pressure on the American colonies to purchase British leather items and to use British hides thus restricting the free sourcing and manufacturing of leather. The designs and styles of leather were gaining popularity commercially all over the world. France manufactured high-fashion shoes while Spain made refined leather armor.
Here are the leather goods that were made during this period:
- Bags
- Shoes and boots
- Satchels
- Hats
- Belts
- Military bags, straps, ties, and other additional items
- Knives, weapons, and swords
- Photo frames (for decorative purposes)
- Binding books
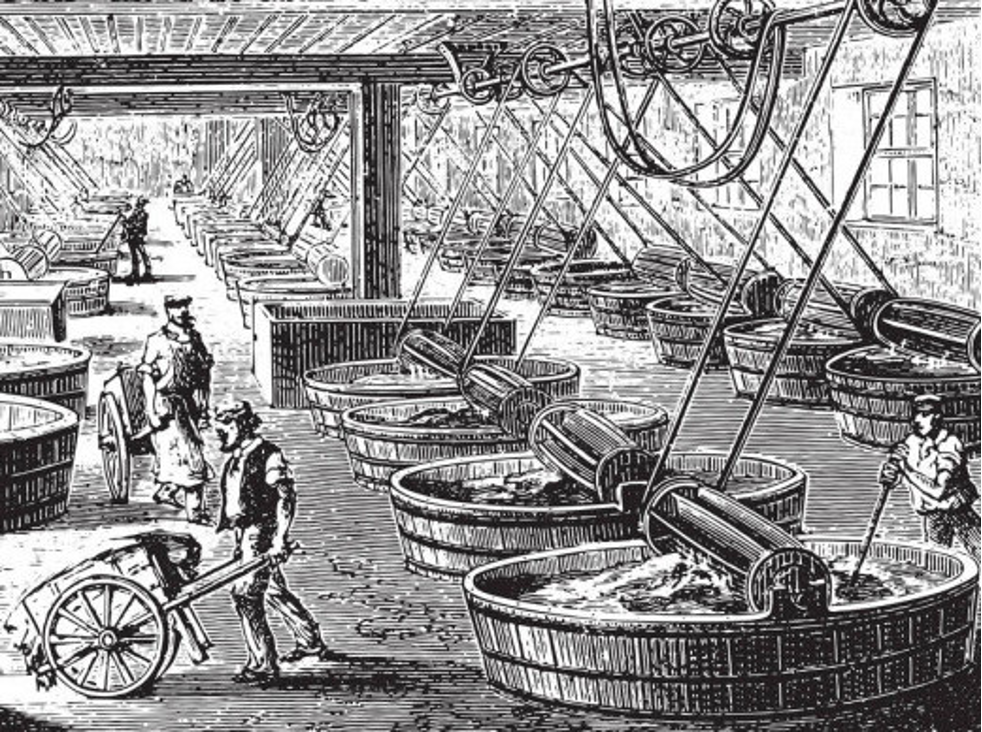
Leather History in the Industrial Revolution (1760 CE – 1840 CE):
Industrial Revolution brings an extensive global change in the history of leather. Mechanized technology was introduced that allowed industries to work more and much faster. This resulted in the need for raw materials and resources to run and maintain machines. Production of such machines was also needed that make steps of manual production more efficient, easy, faster, and accurate.
The leather tanning process was made faster and easier with machines. These machines were also used to split leather (separate the layers of the hides) in such a way that produces smooth, clean, and finished leather.
In 1818, patent leather was developed. It is a type of leather that is coated and has a very high gloss finish. It became popular in making shoes.
During Industrial Revolution, leather was used for every item like before. These items include
- Clothing
- Bags
- Shoes, boots, and laces
- Hats
- Belts
- Military accessories
- Straps
- Ties
- Books
- Horse tack
- Saddlery
- Leather coaches
- Leather carriages, and
- Many other everyday items…
During this period, leather production reached the top of its history around the world.
Leather History in the Victorian Age (1840 CE – 1900 CE):
The victorian age has contributed to the history of leather and leather craft. Let’s take a look at some of these contributions.
In 1858, a method called Chromium tanning or Chrome tan was introduced. It involves the use of minerals and a quick process as compared to vegetable tanning. Chrome tan produced a much softer and thinner leather.
This brought a major shift in leather tanning methods. Chrome tanning became popular with time and eventually, took over vegetable tanning in the overall volume of leather production. In the early 2000s, there was only around 10% of vegetable-tanned leather.
With the rise of chrome-tanned leather production, the market expanded and leather crafters made leather goods for every consumer’s needs.
Moreover, the first faux leather, also called synthetic leather was developed in Germany.
Leather History in the Progressive Era (1900 CE – 1950 CE):
By 1925, in the USA, the average leather tanner had almost 100 employees. At that time, there were about 560 leather tanneries on large scale in the USA.
Mechanized processes were getting so good to such an extent that some of them had replaced the traditional hand-stitching required for some leather items such as shoes, gloves, bags, and books.
The need for employees of using machines increased. Hand skills were overtaken by these powerful machines. However, the quality of machine work couldn’t reach the fine level of some types of hand work.
During the two world wars, technological developments surged leading to a large number of new materials entering the commercial industry. These materials mainly include rubbers and plastics. They would impact the leather industry and the need for leather.
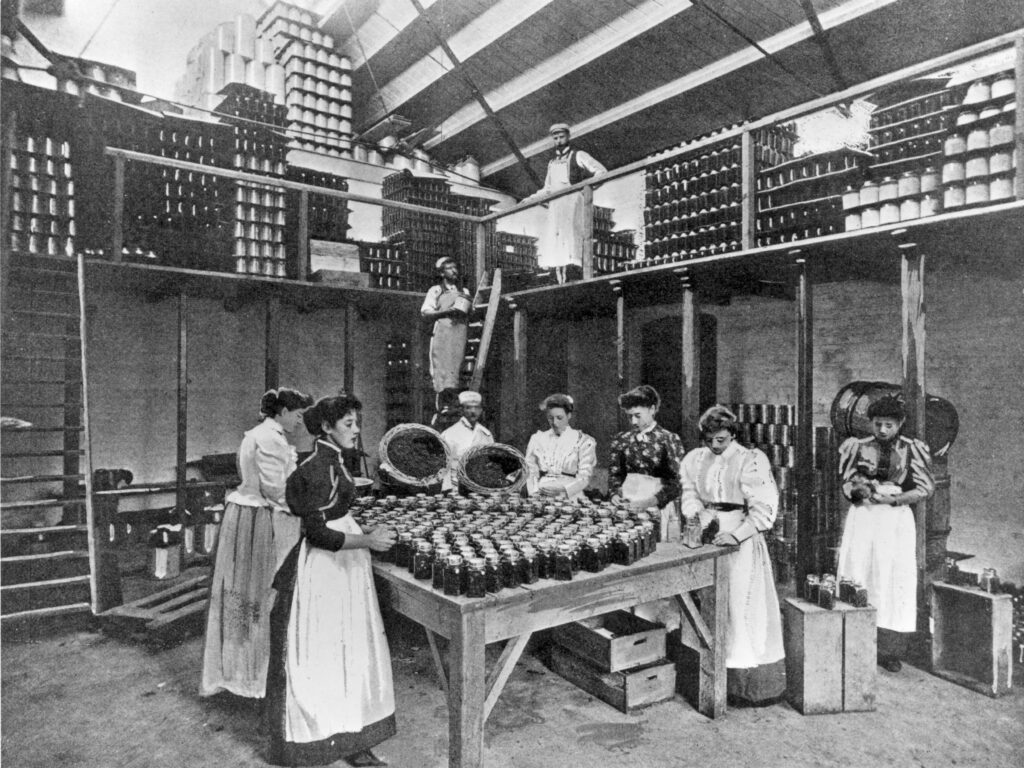

Leather History in the Modern Times (1950 – Present):
After the world wars were over, there was a focus on global stability and prosperity. While the global marketplace surged, there was an increase in imports and exports that included, leather.
In 1963, the first main faux leather was manufactured by DuPont. This synthetic leather was made from a polyester (a plastic fiber) base with a polyurethane (a plastic) coating.
Later on, another synthetic leather was produced, called “leatherette”. It was made by covering fibers with PVC (plastic).
With time, companies start using synthetic leather, plastic, and rubbers for manufacturing products. Naturally, this resulted in a decline in real leather production. Moreover, the global economy shifted to an outsourced model. The theory is to shift leather production to countries with low materials costs and wages. Therefore, this would produce more cost-saving cheap leather.
As a result, leather production shifted to developing countries that can produce it less expensively. As the manufacturers start using raw materials – plastics and rubbers- and leather production shifts to other countries, the flourishing leather industry in the USA has dramatically slowed down.
By 1997, the rate of employment in the leather-related industries fell by about 50%. That is a huge difference from the 1850s when 16% of all the employed workers in the USA worked in the leather-related industries.
Still, in recent times, leather – being the only material – is valued for its unique characteristics and production of high-quality goods used in our day-to-day lives.
That’s the end of an amazing journey!
Such an amazing ride it was! To see the historical journey of leather. To see how leather has evolved through different times, different cultures, and different eras. To see how it helped us to survive, fight wars, win freedoms and drive commercial change globally. To see how it inspired people. Even today, leather has become one of the most essential materials that every one of us has used in one way or another.